pgBackRest: PostgreSQL S3 backups
This tutorial explains how to backup PostgreSQL database using pgBackRest and S3.
Introduction
pgBackRest is a modern PostgreSQL Backup & Restore solution that has all the features you may ever need:
- Parallel backup and restore.
- Full, differential, and incremental backups.
- Delta restore.
- ZSTD compression.
- Encryption.
- And many more.
Installation
Ubuntu provides pre-compiled packages for pgbackrest:
sudo apt install pgbackrest
Terms
Stanza is a pgBackRest configuration for a PostgreSQL database cluster. Most db servers only have one db cluster and therefore one stanza.
Repository is where pgBackRest stores backups and archives WAL segments.
Configuration
Let's create a basic directory structure for configs and logs:
mkdir -m 770 /var/log/pgbackrest
chown postgres:postgres /var/log/pgbackrest
mkdir /etc/pgbackrest
And save the following config in /etc/pgbackrest/pgbackrest.conf:
[demo]
pg1-path=/var/lib/postgresql/14/main
[global]
repo1-retention-full=3 # keep last 3 backups
repo1-type=s3
repo1-path=/s3-path
repo1-s3-region=us-east-1
repo1-s3-endpoint=s3.amazonaws.com
repo1-s3-bucket=s3_bucket_name
repo1-s3-key=$AWS_ACCESS_KEY
repo1-s3-key-secret=$AWS_SECRET_KEY
# Force a checkpoint to start backup immediately.
start-fast=y
# Use delta restore.
delta=y
# Enable ZSTD compression.
compress-type=zst
compress-level=6
log-level-console=info
log-level-file=debug
For point-in-time recovery, you also need to configure PostgreSQL to upload WAL files to S3:
archive_mode = on
archive_command = 'pgbackrest --stanza=demo archive-push %p'
archive_timeout = 300
Full backup
Full backup copies all files in a database cluster.
sudo -u postgres pgbackrest --type=full --stanza=demo backup
Differential backup
Differential backup only copies files that have changed since the last full backup. It is smaller than a full backup, but to restore it you will need the base full backup.
sudo -u postgres pgbackrest --type=diff --stanza=demo backup
Incremental backup
Incremental backup only copies files that have changed since the last backup (full, differential, or incremental). It is smaller than a full or differential backup, but to restore it you will need all dependant backups.
sudo -u postgres pgbackrest --type=incr --stanza=demo backup
Backup restore
To restore the cluster from the last backup:
sudo -u postgres pgbackrest --stanza=demo --delta restore
To view all available backups:
sudo -u postgres pgbackrest --stanza=demo info
PostgreSQL monitoring
To monitor PostgreSQL, you can use OpenTelemetry PostgreSQL receiver that comes with OpenTelemetry Collector.
OpenTelemetry Collector is designed to collect, process, and export telemetry data from multiple sources. It acts as a centralized and flexible data pipeline that simplifies the management of telemetry data in distributed systems.
Uptrace is a OpenTelemetry backend that supports distributed tracing, metrics, and logs. You can use it to monitor applications and troubleshoot issues.
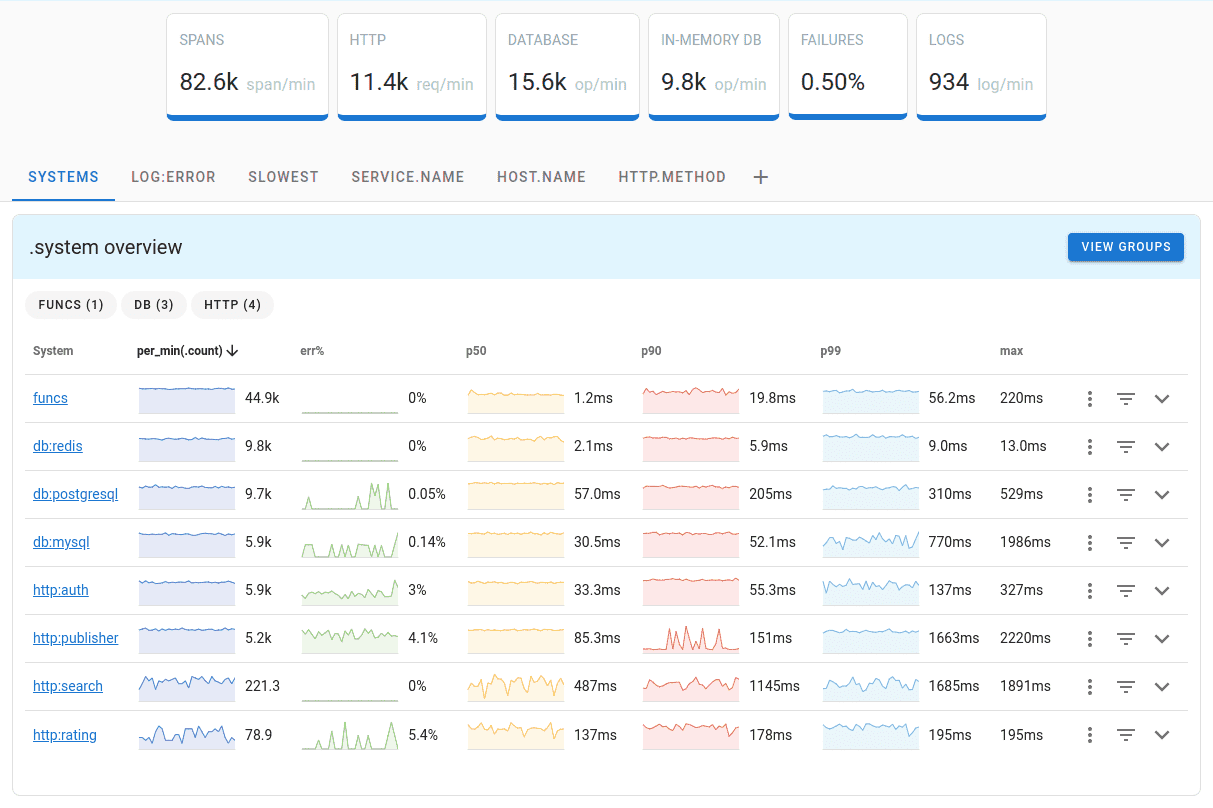
Uptrace comes with an intuitive query builder, rich dashboards, alerting rules with notifications, and integrations for most languages and frameworks.
Uptrace can process billions of spans and metrics on a single server and allows you to monitor your applications at 10x lower cost.
In just a few minutes, you can try Uptrace by visiting the cloud demo (no login required) or running it locally with Docker. The source code is available on GitHub.
Conclusion
pgBackRest is a reliable backup tool that requires miminum configuration. To achieve a good balance between backup size and restoration time, you can create a full backup weekly and a differential/incremental backup daily.
